How to Choose the Best Geomembrane Sheet in Delhi ? Complete Guide
When it comes to engineering marvels that often go unnoticed, geomembrane sheets are at the top of the list. These thin, impermeable sheets play a vital role in a wide range of applications, from environmental protection to industrial containment. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of geomembrane sheets, exploring their versatility, environmental significance, and the critical functions they perform.
What Are Geomembrane Sheets?
Geomembrane sheets are synthetic membranes made from various materials, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). They are manufactured in large rolls and can vary in thickness, depending on their intended use.
Versatility in Applications
Geomembrane sheets have a remarkable ability to adapt to a wide range of applications, making them an essential component in various industries:
1. Environmental Protection:
Landfills: Geomembrane liners are used in landfills to contain waste and prevent leachate, a harmful liquid that can seep into the soil and groundwater, from contaminating the environment.
Wastewater Treatment: These sheets are employed in wastewater treatment facilities to create secure containment structures for the treatment of effluent.
2. Water Management:
Reservoirs and Dams: Geomembranes serve as impermeable barriers in water storage facilities, preventing seepage and maintaining water quality.
Canals and Irrigation: They help control water flow and prevent soil erosion in irrigation canals.
3. Mining and Energy:
Tailings Ponds: In the mining industry, geomembranes are used to construct safe containment ponds for tailings, the waste materials produced during mining operations.
Oil and Gas: Geomembranes are employed in oil and gas exploration to contain hazardous fluids and prevent soil contamination.
4. Agriculture:
Manure Storage: Geomembranes are used in agriculture to create safe storage solutions for animal waste, reducing the risk of groundwater pollution.
5. Construction:
Tunnel Liners: Geomembranes can be used as tunnel liners to prevent water infiltration and soil destabilization during tunnel construction.
Foundations: They are used in building foundations to protect against water infiltration and provide waterproofing.
The Environmental Impact of Geomembrane Sheets
Beyond their versatility, geomembrane sheets offer several significant environmental benefits:
1. Pollution Prevention: One of the primary roles of geomembranes is to prevent pollution. They act as barriers, stopping contaminants from reaching the soil and groundwater, thus protecting these essential resources.
2. Conservation of Water Resources: In water management applications, geomembranes help prevent water loss due to seepage. This conservation is especially critical in arid regions where water is scarce.
3. Soil Erosion Control: Geomembranes in canals and irrigation systems aid in soil erosion control, preserving agricultural land and preventing sedimentation in water bodies.
4. Land Rehabilitation: In mining and industrial settings, geomembranes are used for land rehabilitation, helping to restore disturbed areas and mitigate environmental damage.
5. Reduced Health Risks: By containing hazardous materials in landfills and industrial sites, geomembranes reduce health risks for nearby communities and ecosystems.
The Future of Geomembranes
As environmental concerns continue to grow, the role of geomembranes in safeguarding natural resources and ecosystems becomes increasingly important. The future of geomembranes may involve innovations in materials, construction techniques, and monitoring systems to enhance their performance and sustainability.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): HDPE geomembranes are popular due to their excellent chemical resistance and durability. They are often used in applications where exposure to harsh chemicals or UV radiation is a concern, such as landfill liners and reservoir covers.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC geomembranes are known for their flexibility and resistance to punctures. They are commonly used in applications such as wastewater treatment ponds and decorative pond liners.
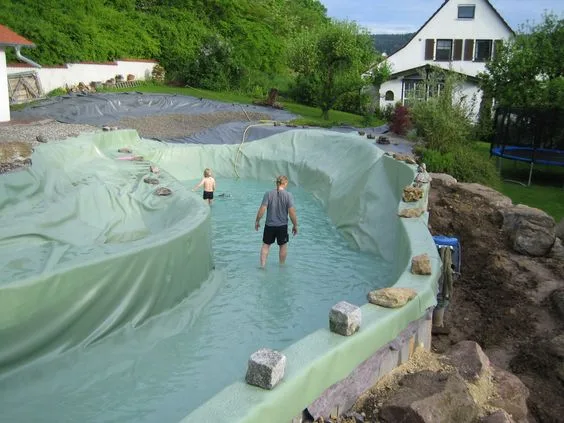
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM): EPDM geomembranes are highly flexible and are often used in applications that require elongation and resistance to extreme temperatures. They are commonly used in pond liners and water containment projects.
Polypropylene (PP): PP geomembranes offer a balance between cost-effectiveness and performance. They are used in various applications, including secondary containment systems and agricultural pond liners.
Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE): CSPE geomembranes are known for their resistance to chemicals and UV radiation. They are used in applications such as hazardous waste containment and industrial water storage.
Butyl Rubber: Butyl rubber geomembranes are valued for their gas impermeability and resistance to ozone and oxidation. They are used in applications like landfill covers and secondary containment.
Sustainable Practices in Geomembrane Usage
With environmental sustainability becoming a paramount concern, the use of geomembranes is evolving to incorporate more environmentally friendly practices:
Recycling: Some geomembrane manufacturers are exploring recycling options for their products. After their intended use, geomembranes can be recycled into new materials, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Biodegradable Geomembranes: Research is ongoing to develop biodegradable geomembranes that can break down naturally over time, reducing the long-term environmental footprint of these materials.
Geomembrane Monitoring: Advanced monitoring systems are being integrated into geomembrane installations to detect leaks or damage early, allowing for timely repairs and reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
Green Infrastructure: In some cases, geomembranes are used in conjunction with green infrastructure practices, such as vegetative covers, to enhance their environmental benefits and promote ecosystem restoration.
The Role of Geomembrane Installers
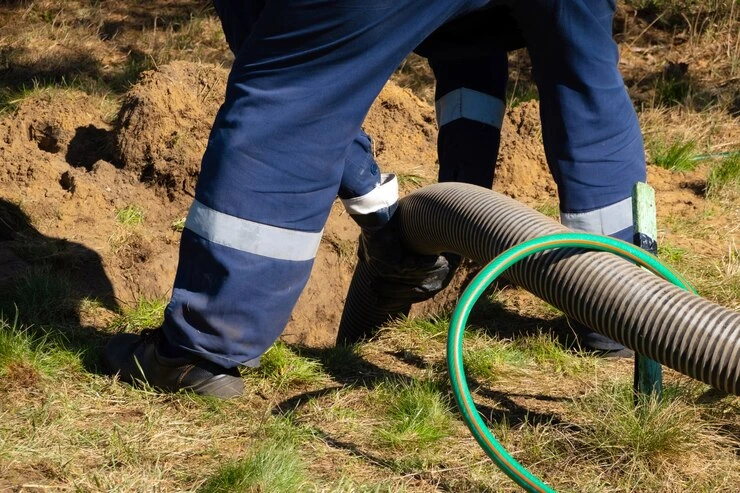
While geomembranes are essential, their proper installation is equally critical to their effectiveness. Geomembrane installers are skilled professionals who ensure that these impermeable barriers are correctly placed and sealed to prevent leaks or seepage.
Key roles of geomembrane installers include:
Site Preparation: They assess the site conditions, including soil type and topography, to determine the appropriate geomembrane material and thickness.
Installation: Geomembrane installers lay and secure the geomembrane sheets according to specific design and engineering guidelines, often using welding techniques to create secure seams.
Quality Control: They conduct quality control checks to ensure that the geomembrane installation is free of defects, wrinkles, or damage that could compromise its integrity.
Sealing and Testing: Proper sealing and testing of seams and connections are critical to prevent leaks. Geomembrane installers are responsible for these crucial tasks.
In conclusion, geomembrane sheets are unsung heroes in diverse applications, providing essential environmental protection, water management, and containment solutions. As technology and sustainability efforts continue to evolve, geomembranes will play an increasingly vital role in safeguarding our environment, conserving resources, and promoting responsible infrastructure development. Their impermeable nature serves as a testament to human ingenuity in finding innovative solutions to some of our most pressing environmental challenges.